效果
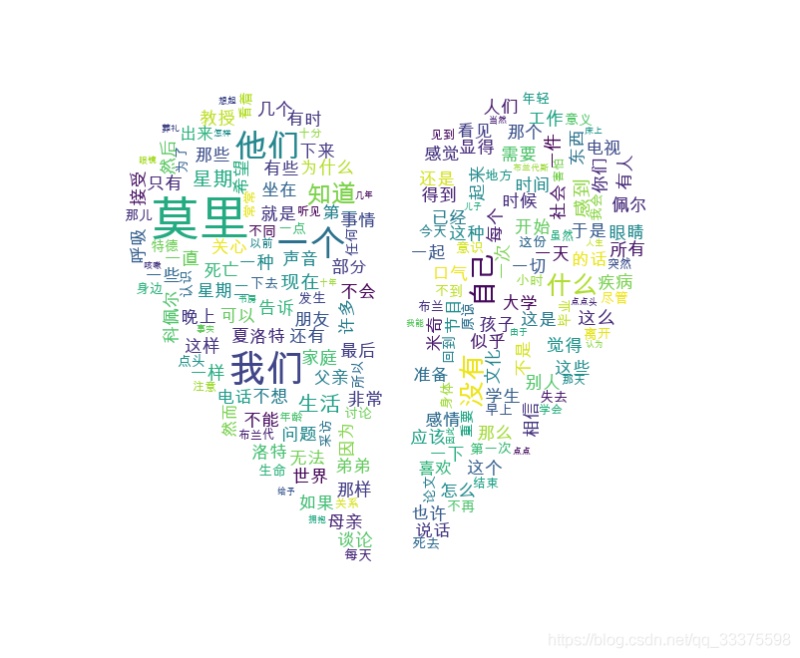

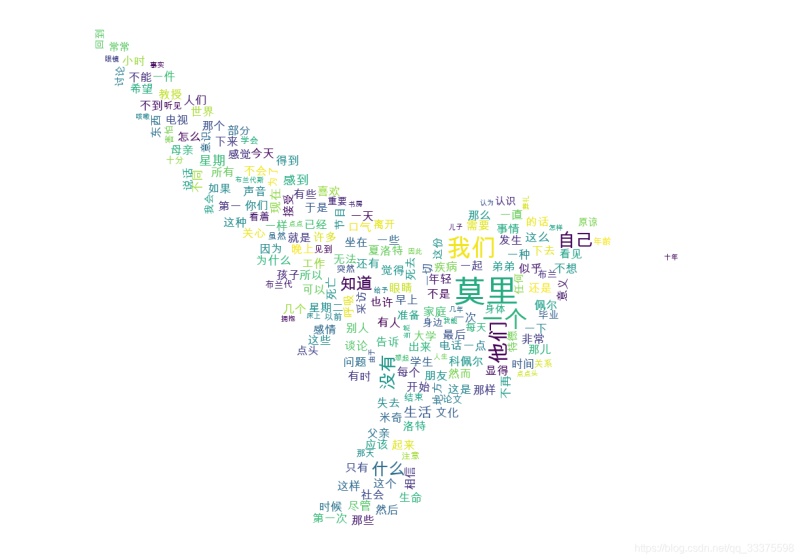
1 實現(xiàn)代碼
讀取txt文件:
def readText(text_file_path):
with open(text_file_path, encoding='gbk') as f: #
content = f.read()
return content
得到文章的詞頻:
def getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content, key_word_need_num = 10, custom_words = [], stop_words =[], query_pattern = 'searchEngine'):
'''
:param text_content: 文本字符串
:param key_word_need_num: 需要的關(guān)鍵詞數(shù)量
:param custom_words: 自定義關(guān)鍵詞
:param stop_words: 不查詢關(guān)鍵詞
:param query_pattern:
precision:精確模式————試圖將句子最精確地切開,適合文本分析;
entire:全模式————把句子中所有的可以成詞的詞語都掃描出來, 速度非常快,但是不能解決歧義;
searchEngine:搜索引擎模式————在精確模式的基礎(chǔ)上,對長詞再次切分,提高召回率,適合用于搜索引擎分詞;
paddle模式————利用PaddlePaddle深度學習框架,訓練序列標注(雙向GRU)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型實現(xiàn)分詞。同時支持詞性標注。
:return:
'''
# jieba.enable_paddle()
# paddle.fluid.install_check.run_check()
if not isinstance(text_content, str):
raise ValueError('文本字符串類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(key_word_need_num, int):
raise ValueError('關(guān)鍵詞個數(shù)類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(custom_words, list):
raise ValueError('自定義關(guān)鍵詞類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(stop_words, list):
raise ValueError('屏蔽關(guān)鍵詞類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(query_pattern, str):
raise ValueError('查詢模式類型錯誤!')
# 添加自定義關(guān)鍵詞
for word in custom_words:
jieba.add_word(word)
if query_pattern == 'searchEngine':
key_words = jieba.cut_for_search(text_content)
elif query_pattern == 'entire':
key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=True, use_paddle=True)
elif query_pattern == 'precision':
key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=False, use_paddle=True)
else:
return []
# print("拆分后的詞: %s" % " ".join(key_words))
# 過濾后的關(guān)鍵詞
stop_words = set(stop_words)
word_count = Counter()
for word in key_words:
if len(word) > 1 and word not in stop_words:
word_count[word] += 1
# res_words = list()
# for data in word_count.most_common(key_word_need_num):
# res_words.append(data[0])
# return res_words
return word_count
繪制圖片:
def drawWordsCloud(word_count, save_img_filePath='', img_mask_filePath=''):
# print(word_count)
# print(type(word_count))
if len(img_mask_filePath) != 0:
img_mask = np.array(Image.open(img_mask_filePath)) #打開遮罩圖片,將圖片轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)組
wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 設(shè)置中文字體,詞云默認字體是“DroidSansMono.ttf字體庫”,不支持中文
background_color="white", # 設(shè)置背景顏色
max_words=200, # 設(shè)置最大顯示的字數(shù)
max_font_size=50, # 設(shè)置字體最大值
random_state=30, # 設(shè)置有多少種隨機生成狀態(tài),即有多少種配色方案
width=400,
height=200,
mask=img_mask
)
else:
wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 設(shè)置中文字體,詞云默認字體是“DroidSansMono.ttf字體庫”,不支持中文
background_color="white", # 設(shè)置背景顏色
max_words=200, # 設(shè)置最大顯示的字數(shù)
max_font_size=50, # 設(shè)置字體最大值
random_state=30, # 設(shè)置有多少種隨機生成狀態(tài),即有多少種配色方案
width=400,
height=200
)
# 繪圖
wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_count) #從字典生成詞云
plt.imshow(wc) #顯示詞云
plt.axis('off') #關(guān)閉坐標軸
plt.show() #顯示圖像
# 保存圖片
if len(save_img_filePath) != 0:
wc.to_file(save_img_filePath)
else:
pass
2 完整代碼
#-*- coding : utf-8-*-
import jieba
from collections import Counter
import paddle
import wordcloud #詞云展示庫
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #圖像展示庫
import time
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def timer(func):
def calculateTime(*args, **kwargs):
t = time.perf_counter()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
print(f'func {func.__name__} coast time:{time.perf_counter() - t:.8f} s')
return result
return calculateTime
def readText(text_file_path):
with open(text_file_path, encoding='gbk') as f: #
content = f.read()
return content
@timer
def getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content, key_word_need_num = 10, custom_words = [], stop_words =[], query_pattern = 'searchEngine'):
'''
:param text_content: 文本字符串
:param key_word_need_num: 需要的關(guān)鍵詞數(shù)量
:param custom_words: 自定義關(guān)鍵詞
:param stop_words: 不查詢關(guān)鍵詞
:param query_pattern:
precision:精確模式————試圖將句子最精確地切開,適合文本分析;
entire:全模式————把句子中所有的可以成詞的詞語都掃描出來, 速度非常快,但是不能解決歧義;
searchEngine:搜索引擎模式————在精確模式的基礎(chǔ)上,對長詞再次切分,提高召回率,適合用于搜索引擎分詞;
paddle模式————利用PaddlePaddle深度學習框架,訓練序列標注(雙向GRU)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型實現(xiàn)分詞。同時支持詞性標注。
:return:
'''
# jieba.enable_paddle()
# paddle.fluid.install_check.run_check()
if not isinstance(text_content, str):
raise ValueError('文本字符串類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(key_word_need_num, int):
raise ValueError('關(guān)鍵詞個數(shù)類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(custom_words, list):
raise ValueError('自定義關(guān)鍵詞類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(stop_words, list):
raise ValueError('屏蔽關(guān)鍵詞類型錯誤!')
if not isinstance(query_pattern, str):
raise ValueError('查詢模式類型錯誤!')
# 添加自定義關(guān)鍵詞
for word in custom_words:
jieba.add_word(word)
if query_pattern == 'searchEngine':
key_words = jieba.cut_for_search(text_content)
elif query_pattern == 'entire':
key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=True, use_paddle=True)
elif query_pattern == 'precision':
key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=False, use_paddle=True)
else:
return []
# print("拆分后的詞: %s" % " ".join(key_words))
# 過濾后的關(guān)鍵詞
stop_words = set(stop_words)
word_count = Counter()
for word in key_words:
if len(word) > 1 and word not in stop_words:
word_count[word] += 1
# res_words = list()
# for data in word_count.most_common(key_word_need_num):
# res_words.append(data[0])
# return res_words
return word_count
def drawWordsCloud(word_count, save_img_filePath='', img_mask_filePath=''):
# print(word_count)
# print(type(word_count))
if len(img_mask_filePath) != 0:
img_mask = np.array(Image.open(img_mask_filePath)) #打開遮罩圖片,將圖片轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)組
wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 設(shè)置中文字體,詞云默認字體是“DroidSansMono.ttf字體庫”,不支持中文
background_color="white", # 設(shè)置背景顏色
max_words=200, # 設(shè)置最大顯示的字數(shù)
max_font_size=50, # 設(shè)置字體最大值
random_state=30, # 設(shè)置有多少種隨機生成狀態(tài),即有多少種配色方案
width=400,
height=200,
mask=img_mask
)
else:
wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 設(shè)置中文字體,詞云默認字體是“DroidSansMono.ttf字體庫”,不支持中文
background_color="white", # 設(shè)置背景顏色
max_words=200, # 設(shè)置最大顯示的字數(shù)
max_font_size=50, # 設(shè)置字體最大值
random_state=30, # 設(shè)置有多少種隨機生成狀態(tài),即有多少種配色方案
width=400,
height=200
)
# 繪圖
wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_count) #從字典生成詞云
plt.imshow(wc) #顯示詞云
plt.axis('off') #關(guān)閉坐標軸
plt.show() #顯示圖像
# 保存圖片
if len(save_img_filePath) != 0:
wc.to_file(save_img_filePath)
else:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
# /Users/mac/Downloads/work/retailSoftware/公司項目/test.txt
text_file_path = "/Users/mac/Downloads/電子書/編程思想/相約星期二/相約星期二.txt"
# text_file_path = "/Users/mac/Downloads/work/retailSoftware/公司項目/test3.txt"
text_content = readText(text_file_path)
# print(text_content)
# print(JNI_API_getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content))
img_mask_filePath = '/Users/mac/Desktop/截屏2021-08-20 下午4.02.10.png'
img_save_filePath = '/Users/mac/Downloads/test9.png'
drawWordsCloud(getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content), img_save_filePath, img_mask_filePath)
到此這篇關(guān)于Python統(tǒng)計詞頻并繪制圖片(附完整代碼)的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Python統(tǒng)計詞頻繪制圖片內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家!
您可能感興趣的文章:- python中Matplotlib繪制直線的實例代碼
- python一繪制元二次方程曲線的實例分析
- python基于turtle繪制幾何圖形
- 淺談Python pygame繪制機制
- 利用Python快速繪制海報地圖