目錄
- 一、文件和異常
- 1.1從文件中讀取數據
- 1.2open()
- 1.3關鍵字with
- 1.4read()
- 二、逐行讀取
- 三、創建一個包含文件各行內容的列表
- 四�、查找字符串中是否含有特定的字符串
- 五�、寫入文件
- 六�、異常
- 6.1處理ZeroDivisionError異常
- 6.2處理FileNotFoundError異常
- 6.3靜默失敗
- 七、存儲數據
- 7.1使用json.dump()和json.load()
- 7.2重構
一、文件和異常
1.1從文件中讀取數據
讀取整個文件
讀取文件先要創建一個文件�,在程序的同一目錄下�。
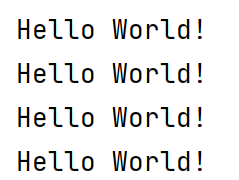
greet.txt
“Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!”
with open('greet.txt') as file_object:
contents=file_object.read()
print(contents)
如果txt文件中有中文�,輸出出現亂碼時,可以with open(‘greet.txt',encoding=‘UTF-8') as file_object:。
1.2open()
要以任何方式使用文件時�,都必須先打開文件�,才能訪問�。函數open()接受一個參數,打開文件的名稱。在這里open(‘greet.txt')返回的是一個表示文件greet.txt的對象�,然后將該對象賦給file_object供以后使用�。
1.3關鍵字with
關鍵字with在不再需要訪問文件后將其關閉�。也可以調用open()和close()來打開文件�。但是不推薦。
1.4read()
方法read()讀取文件的全部內容�,并將其作為一個長長的字符串賦給變量contents�。
二�、逐行讀取
with open('greet.txt',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
for line in file_object:
print(line)

會發現多輸出空白行,文件末尾會有一個換行符�,而print會換行�,所以就多了�,可以使用rstrip()。
with open('greet.txt',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
for line in file_object:
print(line.rstrip())

三�、創建一個包含文件各行內容的列表
with open('greet.txt',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
lines=file_object.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line.rstrip())

3.1readlines()
readlines()從文件讀取每一行�,并將其存在一個列表中�。
四、查找字符串中是否含有特定的字符串
greet_str=''
with open('greet.txt',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
lines=file_object.readlines()
for line in lines:
greet_str+=line
input_str=input('輸入你想查找的字符串')
if input_str in greet_str:
print('有')
else :
print('無')

4.1對字符串進行修改
message='Hello World!'
print(message.replace('World','China'))

五�、寫入文件
5.1寫入空文件
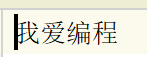
with open('greet.txt','w',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
file_object.write('我愛編程')
w'告訴Python要以寫入模式打開這個文件�。打開文件時可以指定模式:讀取模式'r‘�,寫入模式'w',附加模式‘a'或讀寫模式'r+‘�。如果省略了模式實參�,則默認只讀模式打開文件�。
使用寫入模式時要小心,因為會把文件的內容清空�。
5.2寫入多行
函數write()不會在文本末尾加換行符所以要我們自己添加�。
5.3附加到文件
如果要在文件末尾附加內容�,可以打開附加模式,如果指定文件不存在�,Python將自動創建一個空文件�。
先greet.txt
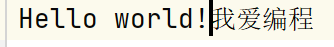
with open('greet.txt','a',encoding='UTF-8') as file_object:
file_object.write('我愛編程\n')
后greet.txt
六�、異常
Python使用稱為異常的特殊對象來管理程序執行期間發生的錯誤。
異常是使用try-except代碼塊進行處理的�。
6.1處理ZeroDivisionError異常
try:
print(4/0)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print('不能數以0')

如果代碼塊try-except后面還有代碼將接著運行�。
try:
print(4/0)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print('不能數以0')
print('--==')

6.2處理FileNotFoundError異常
使用文件時如果找不到文件�,可以使用try-except代碼塊。
分析文本 split()
split()能根據一個字符串創建一個列表�,它以空格為分隔符將字符串拆成多個部分�。
str='你好 世界'
print(str.split())
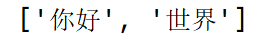
6.3靜默失敗
當發生異常時我們也可以什么都不做。
try:
print(4/0)
except ZeroDivisionError:
pass
pass也可以提示我們什么都沒有做�。
七�、存儲數據
模塊json可以將簡單的數據結構儲存在文件當中�。json
不僅僅能在python中分享數據,也可以給其他編程語言分享�。
7.1使用json.dump()和json.load()
import json
number=list(range(10))
with open('number.json','w') as file:
json.dump(number,file)

json.dump()接受兩個實參:要 儲存的數據和儲存數據的文件對象�。文件通常使用文件擴展名.json來支出文件儲存的數據為JSON格式�。
import json
with open('number.json') as file:
number=json.load(file)
print(number)

7.2重構
將代碼改進的過程稱為重構。重構使代碼更加清晰�,更易于理解�,更容易擴容。
到此這篇關于python基礎之文件和異常處理的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關python文件和異常內容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家�!
您可能感興趣的文章:- 一文搞懂python異常處理�、模塊與包
- Python異常處理與反射相關問題總結
- Python異常處理中容易犯得錯誤總結
- Python打包exe時各種異常處理方案總結
- Python Selenium異常處理的實例分析
- Python pip install之SSL異常處理操作
- 通過實例了解Python異常處理機制底層實現
- Python異常處理機制結構實例解析
- python異常處理之try finally不報錯的原因
- python except異常處理之后不退出,解決異常繼續執行的實現
- python異常處理和日志處理方式
- Python Django中間件�,中間件函數�,全局異常處理操作示例
- Python 異常處理總結